Homogeneous Projection
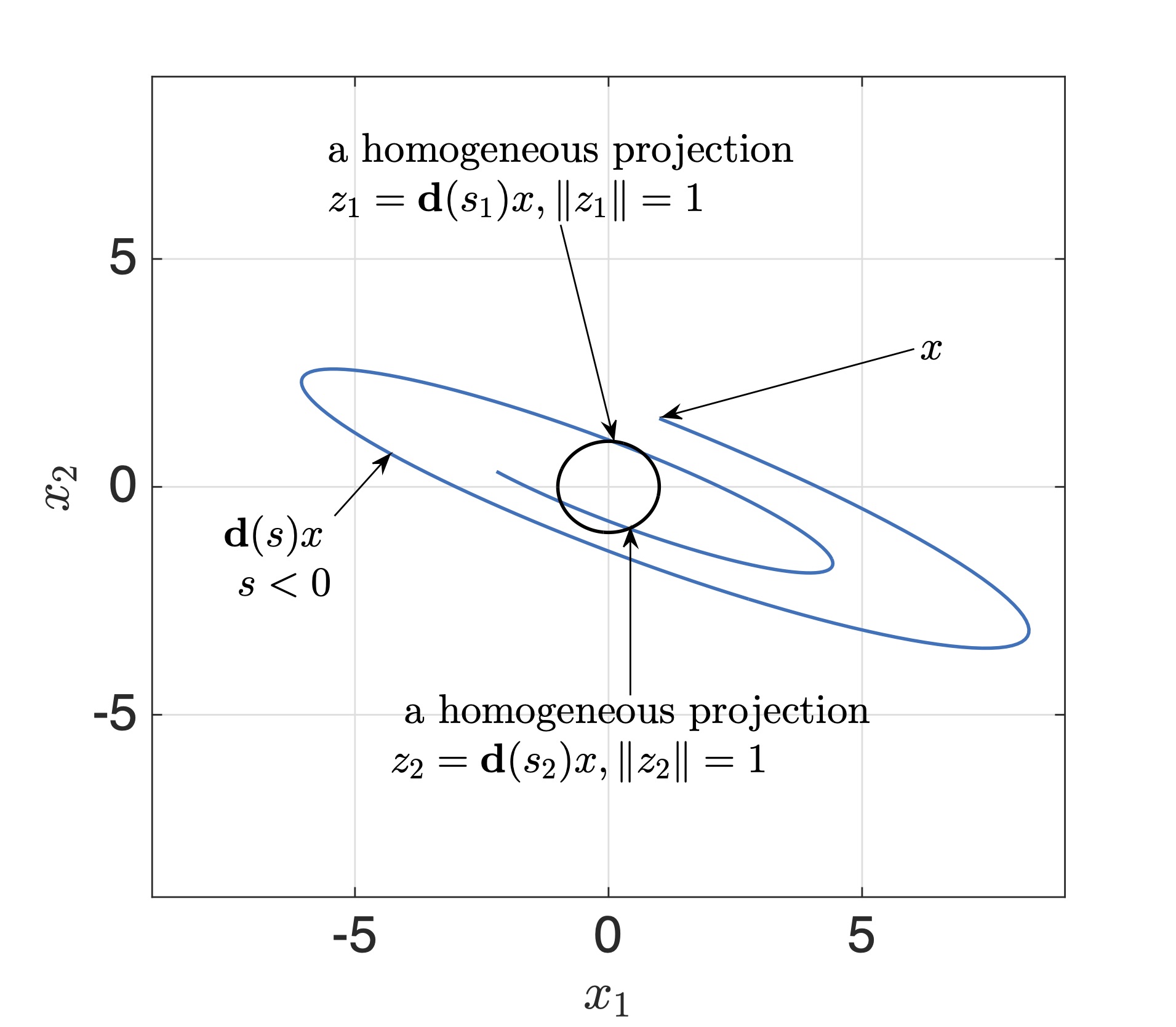
If $\mathbf{ d } $ is a continuous dilation in $ \mathbb{ R } ^n$ then for any $z\in \mathbb{ R } ^n\backslash\{\mathbf{ 0} \}$ there exist $s_0\in \mathbb{ R } $ and $z_0\in S$ such that
$z_0=\mathbf{ d } (s_0)z.$
The corresponding point $z_0\in S$ is called a $\textit{homogeneous projection}$ of $z$ on the unit sphere $S$. $\textbf{If }\mathbf{ d } $ is a monotone dilation then homogeneous projection is unique .
Computation of homogeneous projection
The function ${\color{red} { \texttt{hproj }} } $
- $\textbf{Input parameters}: {\color{blue}x}, {\color{blue}G_{\mathbf{ d } }}, {\color{blue}P} $
- $ \textbf{Output parameters}: {\color{magenta}{z\in }}$ (homogeneous projection of $x$)