State of the Art
The conventional methodology of a control system design is schematically illustrated in Figure 1. It deals with an engineering object (known as a control plant) equipped with some sensors and actuators. Theoretically, as a plant we can consider a drone, a car or its engine separately, a chemical or a bio reactor, a computer or a social network, etc. The sensors in this context are devices which can measure in a real-time some characteristics of the plant (e.g. position, velocity, concentration, density, pressure, flow rate, etc). Actuators, respectively, can influence its behavior (e.g. accelerate a car or turn a rule, add some reagents to a chemical reactor, etc). To control a plant means to influence its behavior so as to achieve a desired goal. The modern engineering practice uses some digital devices (e.g. micro-controllers or industrial computers) for this purpose.
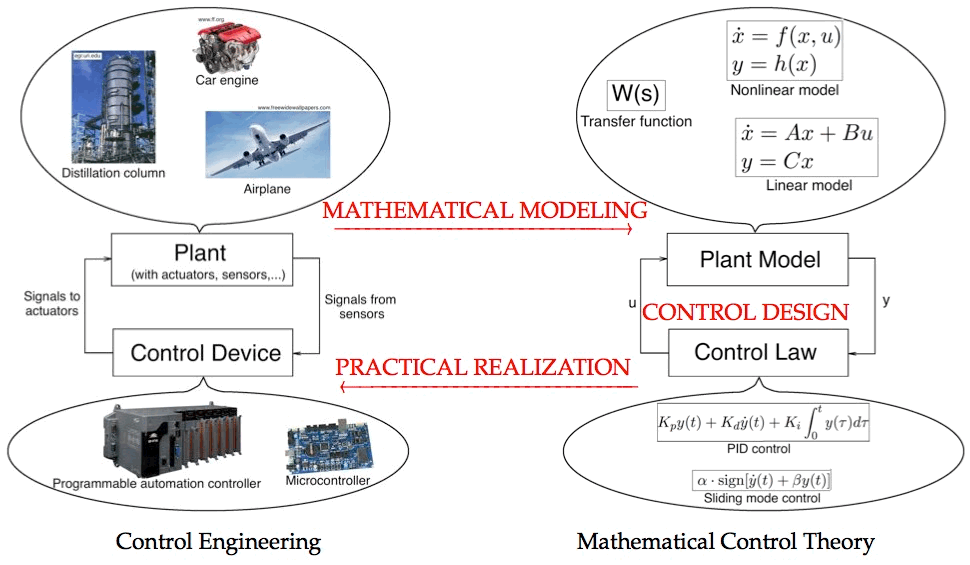
Figure 1. Control Design Methodology
A control algorithm has to be designed for each concrete system and dependently of the control goal. The special area of mathematics called Mathematical Control Theory studies this problem. Instead of a real physical plant it considers its mathematical model (usually a dynamical system) with some input (control signals) and output (sensors measurements) parameters. If the algorithm uses sensors measurements for generation of control signals then it is called a feedback law. This can be a mathematical formula needed to be implemented in the controller (digital device). Prototyping of the control algorithm usually requires a mathematical modeling of the plant, a control design, a digital realization (programming) of the feedback laws and experimental validation of the algorithms. The control design can be based on the model of the system, while, for example, the practical validation can not be done without a direct interaction with a real system. Apart of a mathematical study, a lot of engineering activities accompany the prototyping of control algorithms. ControlHub automatizes the most of them using the modern achievements of computer science and control engineering.